Introduction
Air pollution in Pakistan has reached alarming levels, posing a severe threat to public health, the environment, and the economy. Cities like Lahore are engulfed in toxic smog during winter, rivaling New Delhi in poor air quality. This environmental crisis stems from various human activities, geographic factors, and inadequate policy measures. Understanding the causes, impacts, and potential solutions is critical for mitigating the devastating effects of air pollution on the lives of millions.
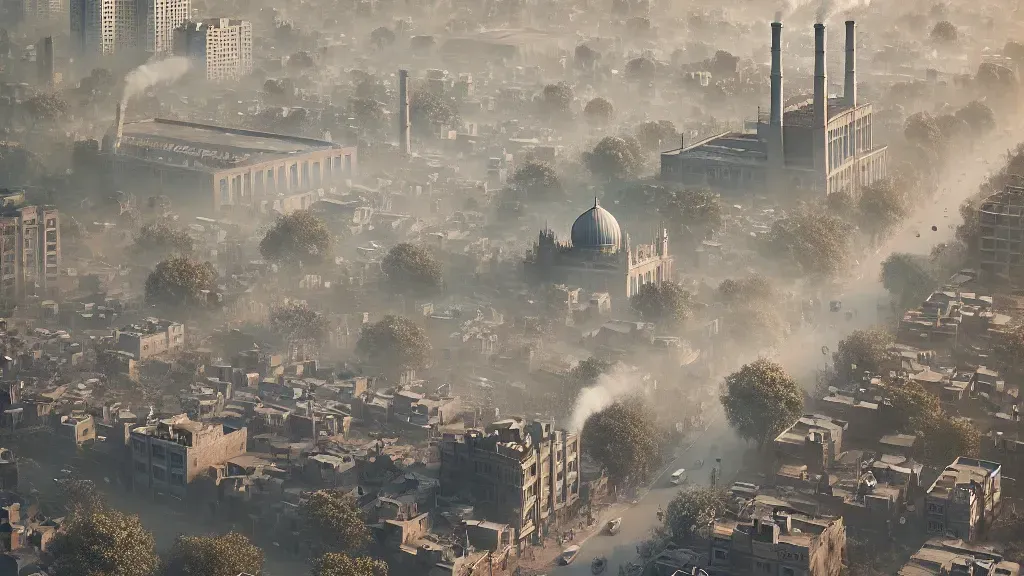

Air quality indices in cities like Karachi, Islamabad, and Peshawar also show concerning trends, indicating that this is not an isolated issue but a nationwide challenge. Tackling this crisis requires a multi-pronged approach that combines science, policy, and community action.
Key Points Overview
Major Causes of Air Pollution in Pakistan:
- Vehicular emissions
- Industrial activities
- Agricultural residue burning
- Urbanization and deforestation
Impacts of Air Pollution:
- Health issues
- Economic burden
- Environmental degradation
Strategies to Combat Air Pollution:
- Policy reforms and enforcement
- Technological advancements
- Public awareness and behavioral change
Detailed Discussion
Major Causes of Air Pollution in Pakistan
1. Vehicular Emissions
Rapid urbanization and the increasing number of vehicles on roads are significant contributors to air pollution in Pakistan. Aging vehicles, poor fuel quality, and inadequate public transportation exacerbate the issue. The absence of stringent emission standards further worsens the problem.
Traffic congestion in major cities like Lahore, Karachi, and Islamabad leads to prolonged idling, which increases emissions of harmful gases. Moreover, the use of two-stroke rickshaws, which are highly polluting, remains prevalent in many areas.
2. Industrial Activities
Industries, especially those in urban areas, emit large quantities of pollutants like carbon monoxide (CO), sulfur dioxide (SO2), and particulate matter (PM2.5). Brick kilns, a common feature in rural and peri-urban regions, rely on low-quality coal, releasing harmful pollutants into the atmosphere.
The lack of proper zoning laws often places industrial units near residential areas, exposing communities to toxic air. Additionally, many industries operate without adequate filtration systems, further contributing to environmental degradation.
3. Agricultural Residue Burning
Farmers in Punjab and Sindh often burn crop residues, releasing massive amounts of smoke and fine particles. This practice intensifies during winter, contributing to the smog that blankets cities like Lahore.
Efforts to introduce alternative methods for managing crop residues, such as using them for bioenergy or organic fertilizers, have been limited in scope. The lack of incentives for farmers to adopt such methods perpetuates the issue.
4. Urbanization and Deforestation
The unplanned expansion of cities and rampant deforestation have reduced green cover, which acts as a natural filter for air pollutants. Urban sprawl increases dust and construction-related emissions, further degrading air quality.
Green spaces in cities are rapidly being replaced by concrete structures, reducing the capacity to absorb carbon dioxide and other pollutants. The unchecked removal of trees for development projects further exacerbates the problem.
Impacts of Air Pollution
1. Health Issues
Air pollution poses severe health risks, including:
- Respiratory Diseases: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, and bronchitis.
- Cardiovascular Problems: Increased risk of heart attacks and strokes.
- Premature Mortality: Exposure to PM2.5 and PM10 particles leads to thousands of premature deaths annually.
- Impact on Vulnerable Groups: Children, pregnant women, and the elderly are disproportionately affected.
Recent studies show a sharp rise in hospital admissions during smog seasons, particularly for respiratory and cardiovascular conditions. Long-term exposure to polluted air has also been linked to developmental issues in children and complications during pregnancy.
2. Economic Burden
The economic cost of air pollution is staggering, estimated at billions of dollars annually. Health expenditures, lost productivity, and reduced agricultural yields contribute to this burden.
In addition to direct costs, air pollution affects tourism, as poor air quality deters visitors. The economic losses extend to decreased labor efficiency, particularly in outdoor occupations such as farming and construction.
3. Environmental Degradation
Air pollution leads to:
- Reduced Visibility: Smog disrupts daily life and transportation.
- Climate Change: Pollutants like black carbon and methane accelerate global warming.
- Loss of Biodiversity: Toxic air impacts ecosystems and wildlife.
The deposition of pollutants on soil and water bodies alters their chemistry, affecting agriculture and aquatic life. Over time, these changes can lead to long-term environmental imbalances that are difficult to reverse.
Strategies to Combat Air Pollution
1. Policy Reforms and Enforcement
- Strengthening Environmental Laws: Implement stricter emission standards for vehicles and industries.
- Monitoring and Accountability: Establish real-time air quality monitoring systems and enforce penalties for violators.
- Sustainable Urban Planning: Promote green infrastructure and regulate construction activities.
Pakistan’s environmental regulatory bodies, such as the Pakistan Environmental Protection Agency (Pak-EPA), need enhanced capacity and autonomy to enforce existing laws. International collaboration for technical and financial support can also play a significant role.
2. Technological Advancements
- Cleaner Fuels and Vehicles: Transition to Euro 5 fuel standards and promote electric vehicles (EVs).
- Industrial Upgrades: Encourage cleaner production technologies and renewable energy sources.
- Waste Management: Develop systems for recycling agricultural residue into bioenergy.
The introduction of hybrid and electric buses in urban centers can significantly reduce vehicular emissions. Similarly, modernizing brick kiln technologies with zigzag methods has shown promising results in reducing emissions.
3. Public Awareness and Behavioral Change
- Educational Campaigns: Inform citizens about the health impacts of air pollution and ways to reduce it.
- Community Initiatives: Support tree plantation drives and local clean-up efforts.
- Behavioral Changes: Encourage the use of public transport and carpooling to reduce vehicular emissions.
Social media platforms can be effectively utilized to spread awareness and mobilize community efforts. Schools and universities can integrate environmental education into their curriculums to instill eco-friendly habits from a young age.
Conclusion
Air pollution in Pakistan is a multifaceted crisis that demands immediate attention. Addressing this issue requires a combination of policy interventions, technological innovations, and public participation. By taking concerted action, Pakistan can improve air quality, safeguard public health, and pave the way for sustainable development.
The path forward must include collaboration between government agencies, non-governmental organizations, and international partners. Only through collective efforts can Pakistan hope to overcome this environmental challenge and ensure a healthier future for its citizens.
FAQs
Q1: What are the main causes of air pollution in Pakistan?
A1: The primary causes include vehicular emissions, industrial activities, agricultural residue burning, and urbanization.
Q2: How does air pollution affect health?
A2: Air pollution causes respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, increases the risk of premature death, and disproportionately impacts vulnerable groups like children and the elderly.
Q3: What measures can reduce air pollution in Pakistan?
A3: Effective measures include implementing stricter environmental laws, promoting clean energy technologies, raising public awareness, and encouraging behavioral changes like carpooling and public transport use.
Q4: Why is Lahore’s air quality so poor?
A4: Lahore experiences severe air pollution due to vehicular emissions, industrial activities, crop burning in nearby regions, and geographic factors that trap pollutants.
Q5: How can individuals contribute to reducing air pollution?
A5: Individuals can reduce air pollution by using public transport, carpooling, conserving energy, and participating in tree plantation drives.
Q6: Are there any successful examples of combating air pollution in other countries?
A6: Yes, countries like China have significantly improved air quality through strict regulations, advanced monitoring systems, and public awareness campaigns. Pakistan can learn from these models to implement effective solutions.
Q7: What role can technology play in reducing air pollution?
A7: Technology can facilitate cleaner production processes, efficient waste management, and the transition to renewable energy. Electric vehicles and modern industrial equipment also contribute to reducing emissions.