Introduction
As we approach 2025, the global community is increasingly concerned about the escalating impacts of climate change. The evidence is undeniable: global weather patterns are shifting, and extreme weather events are becoming more frequent and intense. The question on everyone’s mind is whether we are nearing a critical tipping point—a point of no return. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the projected global weather scenarios for 2025, analyze the global warming trends, and examine the potential for irreversible changes. We’ll delve into future weather predictions, the impact of climate change worldwide, and the urgent need for global action.
Key Points Overview
By 2025, we anticipate:
- A significant increase in the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, including heatwaves, floods, droughts, and wildfires.
- Continued escalation of rising global temperatures, potentially leading to record-breaking years.
- Disproportionate impacts on vulnerable regions, such as coastal areas, small island nations, and developing countries.
- The looming threat of potential tipping points, which could trigger irreversible changes in Earth’s systems, such as melting ice sheets and altered ocean currents.
- An urgent and critical need for enhanced mitigation and adaptation strategies on a global scale.
Detailed Discussion
Rising Global Temperatures and Future Weather Predictions
The relentless rise in global temperatures remains a primary concern. Scientific data consistently demonstrates an upward trajectory, with each year potentially surpassing previous records. Future weather predictions based on advanced climate models suggest that 2025 may witness unprecedented heatwaves and shifts in regional climates. The impact of climate change worldwide is becoming increasingly evident, manifesting as rising sea levels, melting glaciers, and erratic precipitation patterns.
Analyzing Global Warming Trends with Precision
Detailed analysis of global warming trends reveals a consistent increase in average temperatures. This trend is primarily attributed to the accumulation of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, predominantly carbon dioxide, resulting from human activities. The consequences are far-reaching, affecting agricultural yields, ecosystem stability, and human health. Understanding these trends is critical for developing effective mitigation strategies.
Enhancing Future Weather Predictions Through Advanced Modeling
Sophisticated climate models are employed to generate future weather predictions. These models integrate a wide range of data, including atmospheric conditions, ocean currents, and land surface changes. The projections indicate a heightened frequency of extreme weather events and significant alterations in regional climates. While these models are continually refined, the overarching trend remains alarming.
Extreme Weather Events in 2025: A Looming Crisis
Extreme weather patterns 2025 are projected to be a major source of concern. The frequency and intensity of events like heatwaves, floods, and droughts are expected to escalate. These events will have devastating consequences for communities, economies, and ecosystems worldwide.
The Escalation of Heatwaves and Droughts
The ongoing rise in global temperatures contributes to the increased frequency and intensity of heatwaves. Droughts are also becoming more prevalent, leading to severe water shortages and agricultural disruptions. The impact of climate change worldwide is acutely felt in regions already prone to water scarcity.
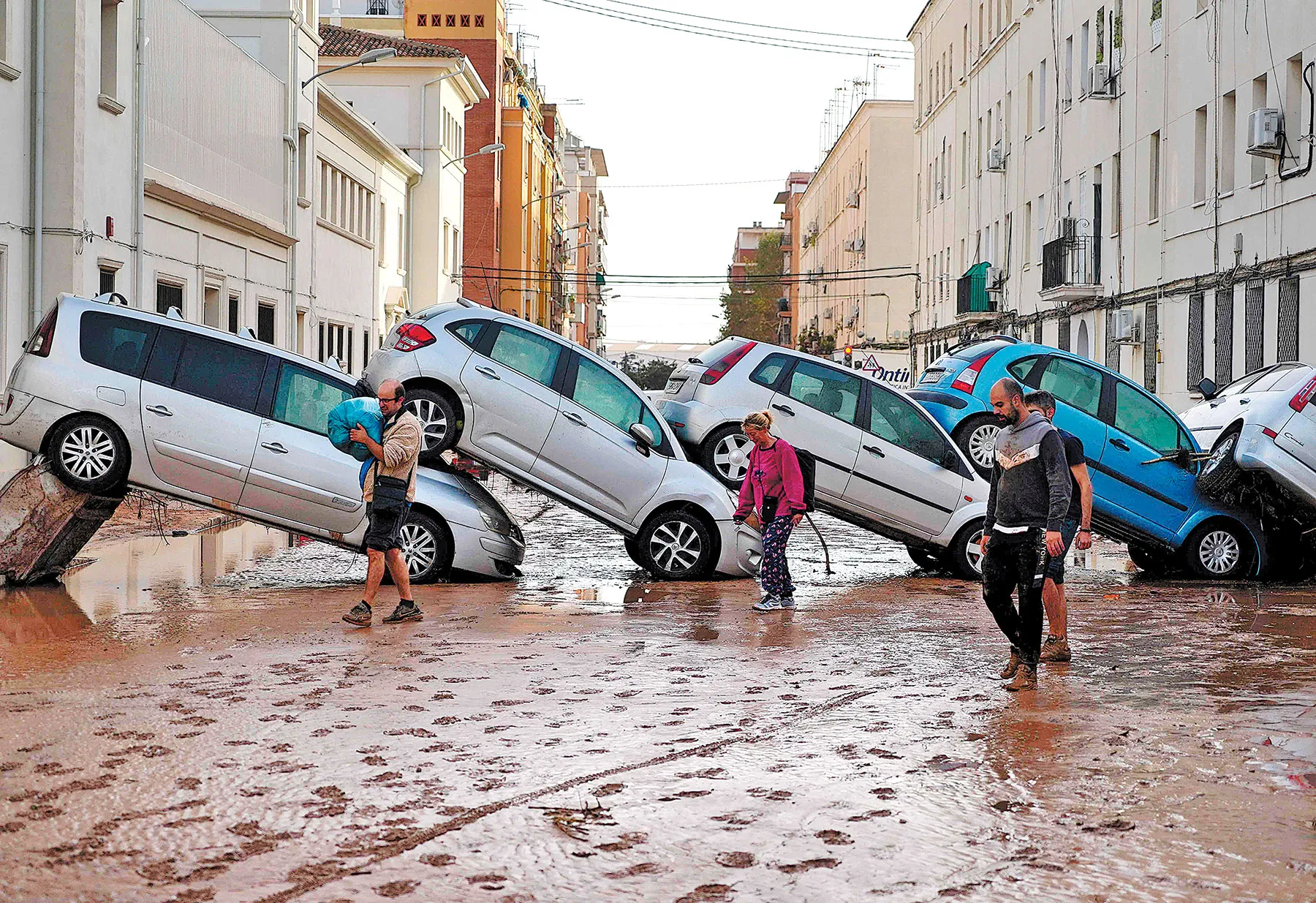
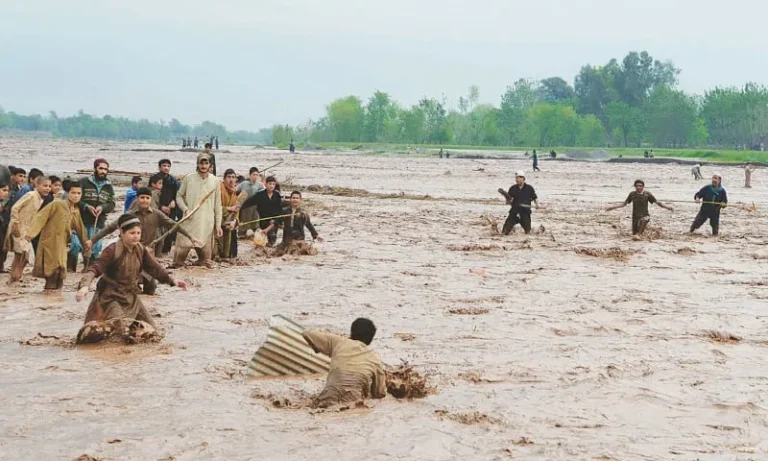
The Intensification of Floods and Storms: A Growing Threat
Climate change is altering precipitation patterns, resulting in more intense rainfall and flooding. Coastal areas are particularly vulnerable to rising sea levels and storm surges. Extreme weather patterns 2025 will likely feature more powerful storms and devastating floods, posing a significant threat to infrastructure and human lives.
The Devastating Impact of Wildfires and Ecosystem Disruptions
Droughts and heatwaves create ideal conditions for wildfires. These fires can have catastrophic consequences for ecosystems and human communities. The destruction of forests also releases substantial amounts of carbon dioxide, further exacerbating climate change.
Impact of Climate Change Worldwide: A Global Perspective
The effects of climate change are not uniform. Vulnerable regions, such as small island nations and developing countries, face disproportionate risks. Rising sea levels threaten coastal communities, while changes in precipitation patterns affect agricultural productivity and food security.
The Vulnerability of Coastal Areas and Small Island Nations: An Existential Threat
Rising sea levels and storm surges pose an existential threat to coastal areas and small island nations. Many communities face the prospect of displacement and loss of land. The impact of climate change worldwide is particularly severe in these vulnerable regions.
The Effects on Agriculture and Food Security: A Global Challenge
Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns affect agricultural yields, threatening food security. Droughts, floods, and heatwaves can damage crops and disrupt food supply chains. Addressing these challenges requires sustainable agricultural practices and resilient food systems.
The Impacts on Ecosystems and Biodiversity: A Loss for All
Climate change is altering ecosystems and threatening biodiversity. Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns can disrupt ecological processes and lead to species extinctions. The loss of biodiversity has far-reaching consequences for ecosystem services and human well-being.
Potential Tipping Points and Irreversible Changes: A Call for Caution
One of the most concerning aspects of climate change is the possibility of reaching tipping points. These are thresholds beyond which changes in Earth’s systems become irreversible. Examples include the melting of ice sheets, the thawing of permafrost, and changes in ocean currents.
The Accelerating Melting of Ice Sheets and Sea Level Rise
The melting of ice sheets in Greenland and Antarctica is a major contributor to sea level rise. If these ice sheets continue to melt at an accelerated rate, the consequences for coastal communities will be catastrophic.
The Thawing of Permafrost and the Release of Methane
Permafrost contains large amounts of frozen organic matter. As it thaws, it releases methane, a potent greenhouse gas. This feedback loop can accelerate global warming trends and lead to further permafrost thawing.
The Disruption of Ocean Currents and Circulation: A Global Shift
Ocean currents play a crucial role in regulating global climate. Changes in ocean circulation can have significant impacts on regional climates and global weather patterns. The disruption of these currents could lead to abrupt and unpredictable changes.
Urgent Need for Mitigation and Adaptation: A Global Imperative
Addressing the challenges of climate change requires urgent action on multiple fronts. Mitigation efforts focus on reducing greenhouse gas emissions, while adaptation measures aim to build resilience to the impacts of climate change.
Enhanced Mitigation Strategies and the Reduction of Emissions
Transitioning to renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, and adopting sustainable land use practices are essential for reducing greenhouse gas emissions. International cooperation and policy measures are crucial for achieving these goals.
Robust Adaptation Measures and Building Resilience
Adaptation measures include developing drought-resistant crops, building flood defenses, and implementing early warning systems. These measures help communities and ecosystems cope with the impacts of climate change.
Strengthening Global Cooperation and Policy Measures
Addressing climate change requires global cooperation and coordinated policy measures. International agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, provide a framework for action. Governments, businesses, and individuals all have a role to play in mitigating and adapting to climate change.
Conclusion
The year 2025 represents a critical juncture in our efforts to combat climate change. The projected increase in extreme weather events and the continued rise in global temperatures underscore the urgency of addressing this challenge. By understanding the impact of climate change worldwide and taking decisive action, we can mitigate the risks and build a more sustainable future. Future weather predictions provide a stark warning, and we must act accordingly.
FAQs
Q1: What are the main drivers of rising global temperatures?
A1: The primary driver is the increase in greenhouse gas emissions, particularly carbon dioxide, from human activities such as burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes.
Q2: How will extreme weather patterns 2025 affect different regions?
A2: Coastal areas will face increased flooding and storm surges, while inland regions may experience more frequent and intense heatwaves and droughts. Vulnerable regions like small island nations and developing countries will be disproportionately affected.
Q3: What are potential tipping points in climate change?
A3: Tipping points include the melting of ice sheets, the thawing of permafrost, and changes in ocean currents. These are thresholds beyond which changes in Earth’s systems become irreversible.
Q4: What can individuals do to mitigate climate change?
A4: Individuals can reduce their carbon footprint by conserving energy, using sustainable transportation, adopting a plant-based diet, and supporting sustainable businesses.
Q5: What are the key adaptation measures for climate change?
A5: Adaptation measures include developing drought-resistant crops, building flood defenses, implementing early warning systems, and promoting sustainable land use practices.
Q6: Where can I find reliable information regarding future weather predictions?
A6: Reputable sources of information include the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), and the World Meteorological Organization (WMO).